Overview
The City of Boulder's transportation strategy sets out a roadmap for a future that is shared and electric to meet our transportation and climate goals.
Electric micromobility can help us get there.
Electric micromobility — like e-bikes, e-scooters and e-skateboards — are an important part of Boulder’s transportation network, helping connect people to places and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The City of Boulder's transportation strategy sets out a roadmap for a future that is shared and electric to meet our transportation and climate goals.
Electric micromobility can help us get there.
Use the guide below to know what you ride and where you ride.
| VEHICLE TYPE/CLASS | SIDEWALKS* | MULTI-USE PATHS | STREETS & BIKE LANES | Trails |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Class 1 and 2 E-bike (max speed of 20 mph) 
| ✔️* | ✔️ | ✔️ | Yes, only on certain OSMP trails. |
Class 3 E-bike (max speed of 28 mph) 
| ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ |
Low-Power Scooter 
| ❌ | ❌ | Streets: ✔️ Bike Lanes: ❌ | ❌ |
Toy Vehicle 
| ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Lightweight Electric Vehicle 

| ✔️* | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |

E-motos are not allowed on Boulder's transportation system. While the term "e-motos" is not currently defined in Boulder Revised Code, you can think of them as Toy Vehicles depending on the size of motor, watt output and other specifications. View definitions.
| Feature | Class 1, 2 or 3 Electric Bicycle | E-Moto |
|---|---|---|
| Operable Pedals | Required | Not required (often unoperable) |
| Motor Power | ≤ 750W | > 750W (some models up to 6,000W) |
| Top Speed | ≤ 20-28 mph | 30-65+ mph |
| Throttle | Class 2 only (≤ 20 mph) | Usually throttle only |
| Licensing/Registration | No | Required |
| Product Category | Consumer Product | Motor Vehicle (requires license, registration, insurance) |
| Street Legal for Minors |
| No, unless the device is registered, licensed, and insured, and the rider meets minimum age requirements. |
You can also watch the E-Bike Buying Guide in Spanish.
Micromobility, such as bikes, scooters and skateboards, is a wheeled type of transportation that is:
Low speed
Operated by a single person
Meant for travel over a short distance
Privately owned or available as shared, rental vehicles
E-micromobility, or electric micromobility, is a type of micromobility that is also:
Powered by electricity
Does not have an internal combustion engine
Does not travel over 20 mph
Examples include e-bikes, e-scooters and e-skateboards.
Manufacturers will often describe devices as Class 1-3 e-bikes due to their ability to toggle between power settings.
Because these devices can speed more than 20+ miles per hour, their use is more restricted than Class 1 and 2 e-bikes.
Read the regulations below to know if your device is defined in the Boulder Revised Code as a Class 3 e-bike, Low-Power Scooter or other device.
Following the completion of a community engagement process, visitors are now allowed to ride Class 1 and Class 2 electric bikes on certain open space trails. View a map of specific trails for Class 1 and 2 e-bikes.
Read our guide to learn more about the types of e-bikes allowed on Open Space and Mountain Parks trails and where you can ride them:
Depending on the bike, you might find this information in the owner’s manual or manufacturer's website.
According to state law, a motorcycle is a motor vehicle that uses handlebars and is not a low-speed electric vehicle or low-power scooter. To be “roadworthy,” or street legal, a motorcycle must have head lamps, tail lamps and reflectors, stop lamps, brakes, horns, mufflers, mirrors, tires marked for DOT on-road use, a vehicle identification number (VIN), and a certified VIN inspection. For more information, visit the Colorado Division of Motor Vehicles Roadworthy Motorcycle Checklist.
E-motos do not have any of this equipment despite their higher speeds, which means they are not street-legal. Regardless, e-motos can't be used on sidewalks, multi-use paths or bike lanes.
However you roll, please consider your neighbors and Share the Path.
A white light in front and a red light on the back.
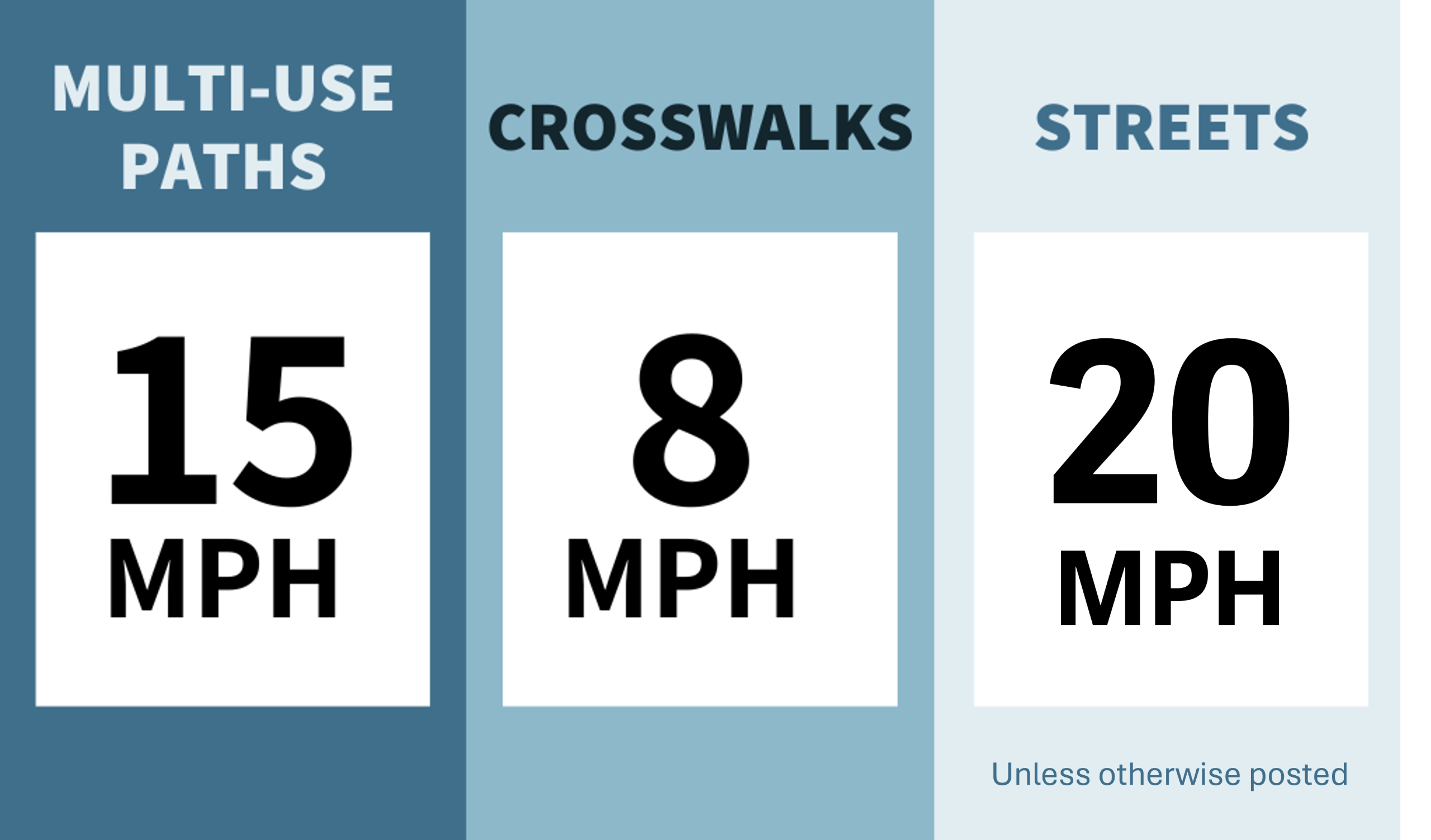
When riding on roads and bike lanes, remember:
Ride single file. Only ride side-by-side with no more than one other person, if safe to do so and if you're not disrupting the flow of traffic.
Ride predictably.
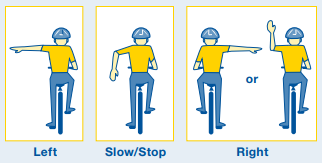
People on e-bikes and bikes who are 16 or older can use Colorado’s Safety Stop as long as they do not take the right of way from another road user. If it is your right of way, you may treat stop signs as yield signs, and red lights like stop signs, and stop signs like yield signs.
For full Electric Mobility Device Definitions per the Boulder Revised Code, view the City of Boulder Municipal Code. Some laws are also under the state's jurisdiction, which you can view on the Colorado Revised Statutes.

Electric assisted bicycle means a vehicle having:
The State of Colorado recognizes three classes of electric-assisted bicycles:
The City of Boulder permits class 1 and class 2 e-bikes on sidewalks (except in dismount zones), multi-use paths, bike lanes and streets. Class 3 e-bikes are permitted only on streets and in bike lanes.


Low-power scooter means a self-propelled vehicle designed primarily for use on the roadways with
Low-power scooter does not include a toy vehicle, bicycle, electric assisted bicycle, electric scooter, or any device designed to assist people with mobility impairments who use pedestrian rights-of-way.

Lightweight electric vehicle means any device capable of moving itself, or of being moved, from place to place upon wheels that is
Lightweight electric vehicle shall not include a toy vehicle.

Low-speed electric vehicle means a vehicle that is self-propelled utilizing electricity as its primary propulsion method:
Such vehicles are motor vehicles and are authorized to operate upon the streets of the city subject to the provisions of the Boulder traffic code.

Toy vehicle means any vehicle that has wheels and is not designed for use on streets or for off-road use.
Includes, but is not limited to, gas-powered or electric-powered vehicles commonly known as mini-bikes, "pocket" bikes, and kamikaze boards.
Toy vehicle does not include lightweight electric vehicles, off-highway vehicles, or snowmobiles.
Toy vehicles are not permitted anywhere on the city's public transportation network.
An Off-Highway Vehicle (OHV), C.R.S. 42-6-102 (11.5), is defined as:
A self-propelled vehicle that is:
Off-highway vehicles do not include:

While Boulder Revised Code does not categorize e-motos, e-motos may be classified as low-power scooters, toy vehicles, or off-highway vehicles (OHV) depending on size of motor, watt output, and other specifications.
They are not considered e-bikes.